
The charge is diluted by the burnt gases due to incomplete scavenging. Thermal efficiency is less than four stroke engine. It requires fewer spare parts due to its simple design. The ports can be easily designed and covered and uncovered by the movement of the piston itself. There is no valve and valve mechanism in it. It is simpler in construction and mechanism. For the same power, a two stroke engine is more compact, light and requires less space than a four stroke engine, therefore is used in motorcycles and scooters. Lighter flywheel is required in two stroke engine because of the more turning moment on the crankshaft. Power developed by the two-stroke engine is twice that developed by the four-stroke engine for the same engine speed and volume. The four stroke engine gives a working stroke for each two revolutions of the crankshaft. Two stroke engine gives a working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft. Port Timing diagram for a two stroke cycle engine We get two strokes for the single revolution of the crankshaft. Finally, the cycle event is then repeated. The cylinder is completely filled with the fresh charge but it is somewhat diluted with the exhaust gases. The piston is now at the BDC position. The charge strikes the deflector on the piston crown, rises to the top of the cylinder and pushes out most of the exhaust gases. As soon as the transfer port opens, the charge through it is forced into the cylinder. Further downward movement of the piston uncovers first the exhaust port and the transfer port and the exhaust starts through the exhaust port. During this stroke the inlet port is covered by the piston and the new charge is compressed in the crankcase. Due to this high-pressure force, the piston moves downward and rotates the crankshaft and does useful work. As soon as the combustion of the fresh charge takes place, a large amount of the hot gases is produced which exerts a very high-pressure force on the top of the piston. 
The ignition of the fresh charge is takes place by the spark plug.
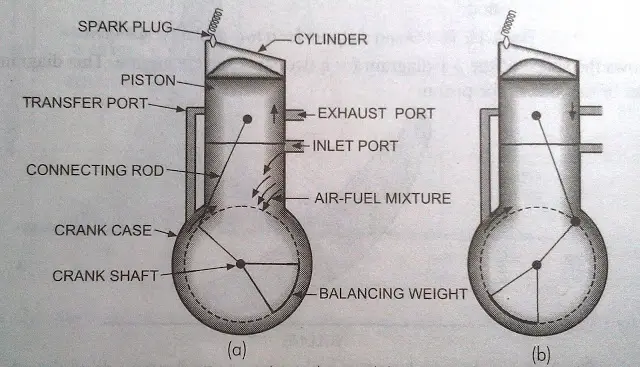 The exhaust port and the inlet port remains covered when the piston at the TDC.
The exhaust port and the inlet port remains covered when the piston at the TDC. 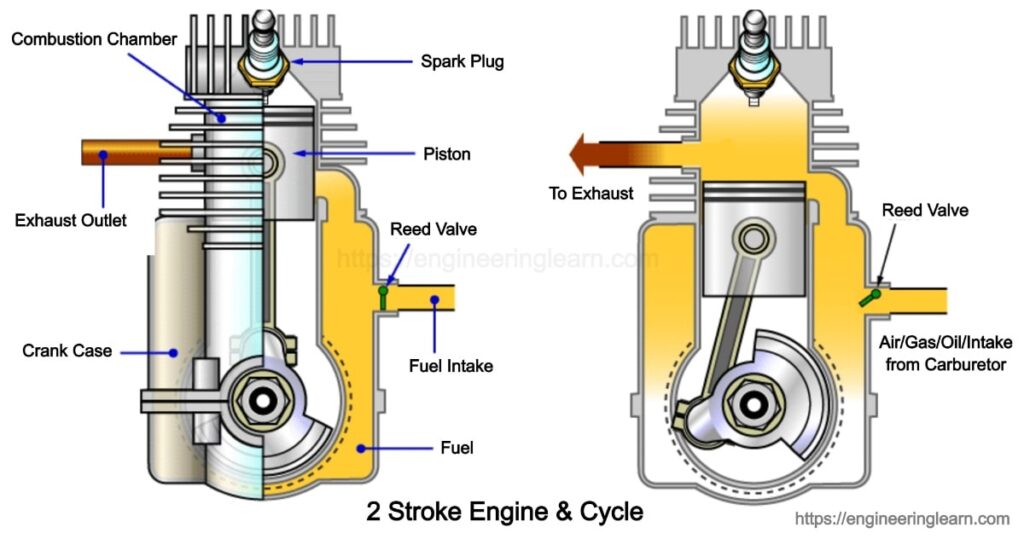
Because of the upward movement of the piston, a partial vacuum is created in the crankcase and this allows the entry of the fresh charge into the crankcase through the uncovered inlet port.During upward stroke, the piston moves from BDC to TDC and compresses the charge (air-fuel mixture) in the combustion chamber of the cylinder.The two strokes of a two stroke engines are described as follows: 1.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
